Have you ever heard of a satellite made of wood? Believe it or not, Japan has launched the world’s first wooden satellite called LignoSat into space! This unique satellite is designed to address a growing problem: space debris.
The Problem of Space Junk
Space debris is any object made by humans that gets left behind in space. This includes old satellites, rocket parts, and even tiny pieces of metal. There are millions of pieces of space debris orbiting Earth, and they pose a serious threat to active satellites and spacecraft. Collisions with debris can damage or even destroy these spacecraft, which can disrupt important services like GPS and communication.
Wooden Satellite to the Rescue
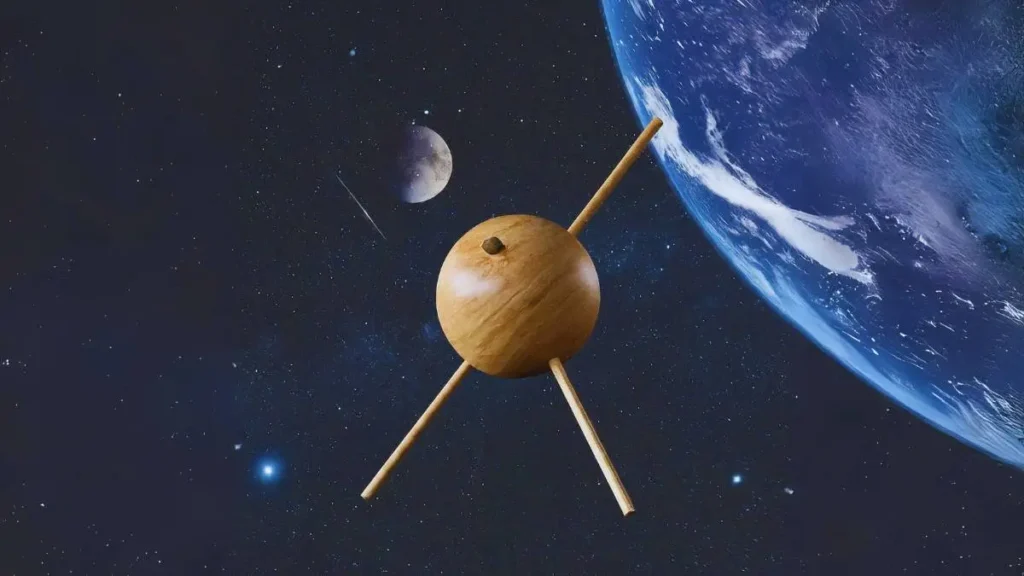

LignoSat is made of a special type of wood called magnolia, which is known for its strength and durability. The satellite is about the size of a coffee mug and weighs only about 10 pounds. It will be launched into space this summer on either an Orbital Sciences Cygnus supply ship or a SpaceX Dragon mission.
Once in orbit, LignoSat will experiment with a new technology called “controlled burn-up.” This technology will allow the satellite to safely burn up in the Earth’s atmosphere at the end of its mission. This is important because traditional satellites are often made of metal, which can take hundreds of years to burn up and can create harmful debris when they do.
Why Wood for a Satellite?
Usually, satellites are made from metals like aluminum because they are strong and can handle really hot and cold temperatures. But here’s the issue: when a satellite finishes its job, it stays up in space, adding to the space junk problem.
Now, we have LignoSat, a new kind of satellite. Instead of metal, it’s mostly made from a tough kind of wood called magnolia. What’s cool about LignoSat is that when it’s done working, it’s designed to burn up completely as it falls back to Earth. This means it won’t leave any more space junk behind.
A Sustainable Future for Space
If LignoSat’s mission is successful, it could pave the way for more sustainable satellites in the future. Wooden satellites could help to reduce the amount of space debris and make space exploration more environmentally friendly.